Automation vs. Robotics: Unraveling the Distinctions for Modern Manufacturing Excellence
In the accelerating currents of modern manufacturing, a lexicon of technological innovation has emerged. Among these, "automation" and "robotics" are often used interchangeably. Yet, for businesses striving for operational excellence, strategic investment, and sustainable growth, a precise understanding of these concepts isn't just academic—it's critical. Let's peel back the layers to dissect automation and robotics, highlighting their unique attributes, symbiotic relationship, and profound impact on the industrial landscape.
Deconstructing the Concepts: What is Automation, Really?
At its heart, automation is simply using technology to get tasks done with minimal human help. Think of it as designing systems, processes, or equipment that can operate on their own, or mostly on their own, following predefined steps or reacting to specific conditions without constant human supervision. The range of automation is incredibly broad:
- Software Superheroes: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools, for instance, are the silent workhorses handling repetitive office tasks: crunching numbers for invoices, updating customer records, or sending out routine emails. No physical robot here, just smart software.
- Industrial Conductors: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are the brains behind complex factory floor machinery, ensuring every action happens with precise timing and sequence.
- Orchestrated Production Lines: Picture entire assembly lines where products glide seamlessly through various stages. Machines handle welding, painting, and inspection, often with human oversight but minimal direct intervention.
The big picture with automation is clear: boost efficiency, ensure consistency, speed things up, and nail down accuracy. At the same time, it drives down operational costs, slashes human error, and frees up your team for more complex, creative, or strategic work. For manufacturers, it's a strategic imperative to scale production, refine product quality, and stay sharp in the global arena.
Deconstructing the Concepts: Unveiling Robotics
Now, while often linked to automation, robotics is a very specific and specialized subset. It's solely about the design, construction, operation, and application of robots. What's a robot? It's a programmable machine built to carry out complex tasks, often with a degree of autonomy and the ability to physically interact with its surroundings.
What makes a robot more than just an automated machine?
- They're Physical: Robots are tangible. They move, they grasp, they perform actions in the real world. They come equipped with various "hands" (end-effectors like grippers, welders, cameras) to engage with their environment.
- They're Reprogrammable: A defining feature of modern robots is their ability to be taught and re-taught new tricks. This flexibility makes them incredibly adaptable when production needs shift or product designs evolve.
- They Sense and Act: Robots typically integrate sophisticated sensor systems—vision, force, touch—to perceive their environment. Then, they use powerful actuators (motors, hydraulics) to execute movements with remarkable precision.
- They Think (A Bit): While some robots follow strict human commands, many are designed to work autonomously, making decisions based on sensor input and predefined rules.
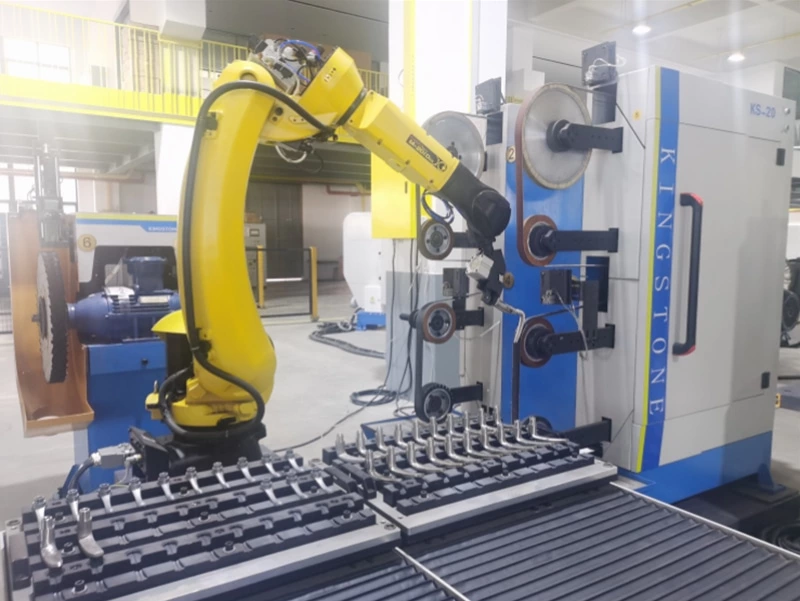
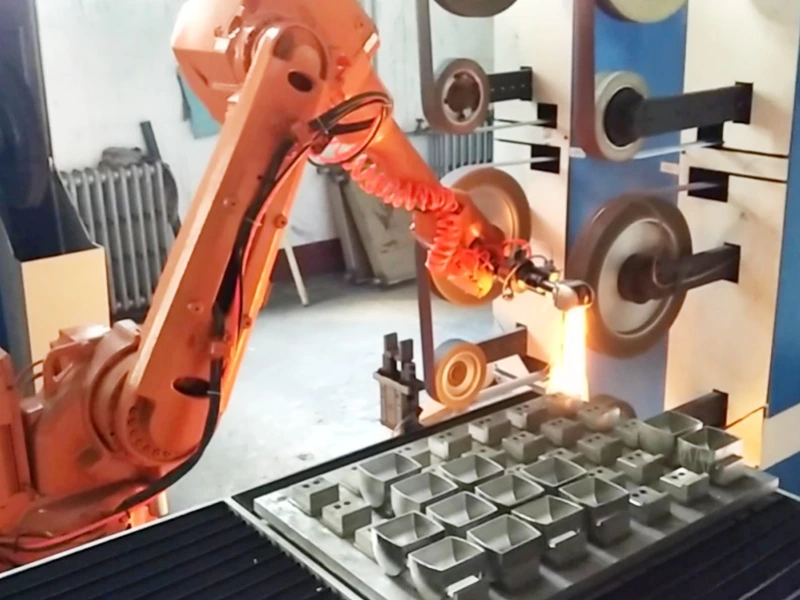
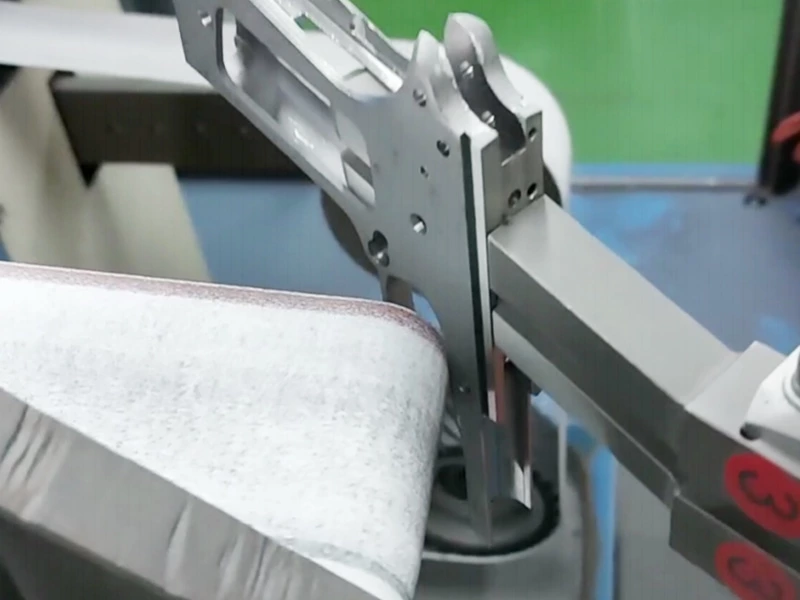
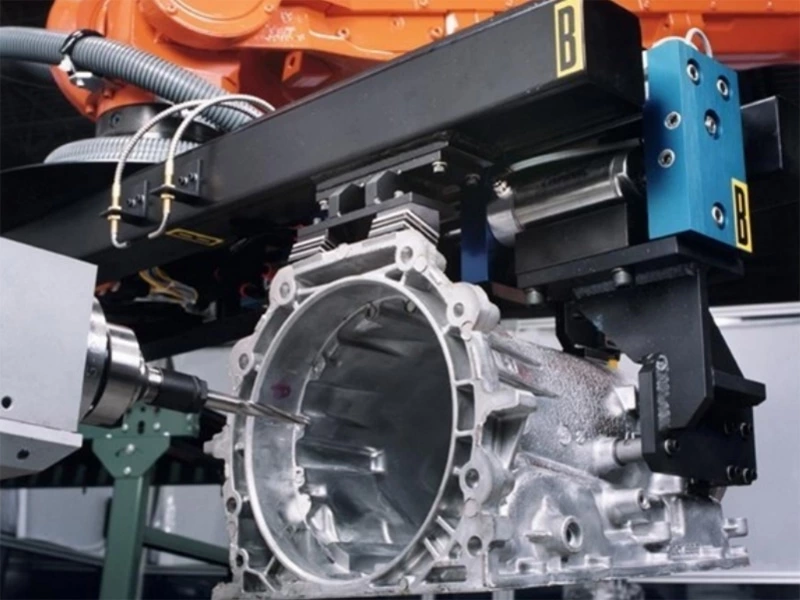
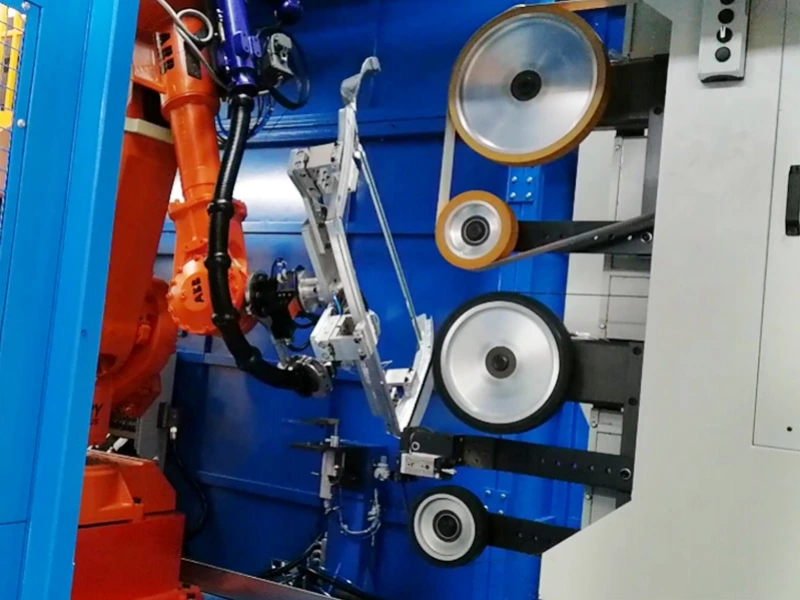
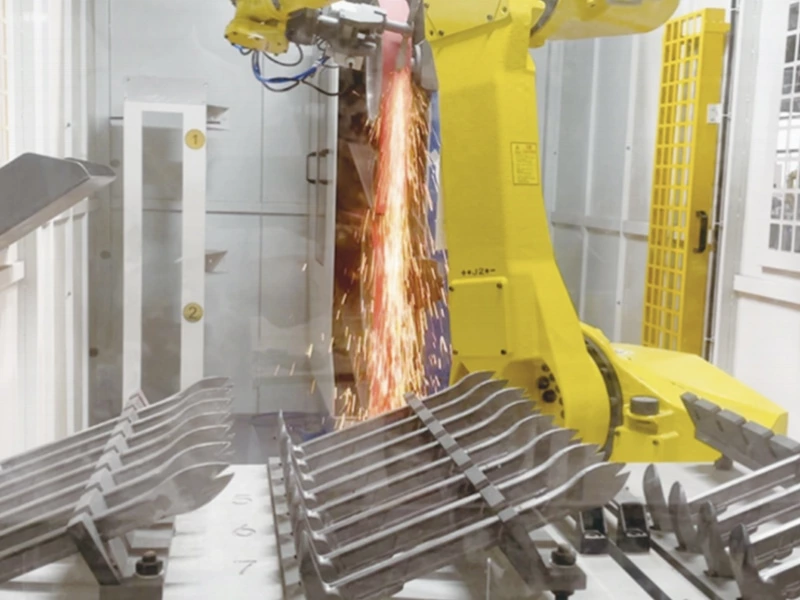
You see robotics everywhere in manufacturing: those articulated robotic arms on an automotive assembly line, the collaborative robots (cobots) gently working alongside human employees, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) ferrying materials through warehouses.
Key Differentiators: A Side-by-Side View
To nail down the difference, let's put them head-to-head:
| Aspect | Automation | Robotics |
| Scope | Broad; reduces human effort in any task. | Specific; programmable physical machines performing complex actions. |
| Physical Form | May not involve physical machines (e.g., software). | Always involves physical machines interacting with the environment. |
| Main Goal | Streamlining processes, boosting efficiency, cutting errors. | Executing physical tasks with precision, consistency, endurance. |
| Flexibility | Varies; some specialized, others adaptable (like RPA). | Inherently flexible; reprogrammable for different tasks. |
| Complexity | Simple mechanical systems to sophisticated AI algorithms. | Complex electromechanical systems, advanced control, integrated sensors. |
| Intervention Level | Aims for minimal human involvement in any task. | Focuses on performing physical tasks with defined autonomy. |
The Symbiotic Relationship: Hand in Glove
While distinct, automation and robotics aren't rivals; they’re partners. Robotics is a powerful type of automation, but remember, not all automation involves robots. This distinction is crucial for smart implementation.
Think about it this way:
- Automation Without a Robot: Imagine a software system that automatically processes online orders, updates your inventory, and sends shipping notifications. That’s automation. No physical robot is involved, yet it dramatically cuts down on manual effort.
- Robotics as Automation: That robotic arm precisely welding car frames? That’s robotics automating the welding task, achieving speed and consistency far beyond what human welders can maintain.
- The Full Integration: A modern smart factory showcases this synergy perfectly. Automated conveyor belts zip components to robotic workstations where robots handle assembly, inspection, and packaging. A central automated control system, often leveraging AI and IoT, orchestrates the entire flow. Here, automation provides the framework, and robotics provides the muscle for specific physical tasks.
In essence, automation sets the "why" and the "how" (the big-picture strategy and process design), while robotics offers a highly capable "tool" (the physical executor) within that broader automation strategy.
The Transformative Benefits in Modern Manufacturing
Strategically weaving together automation and robotics delivers a host of benefits that are fundamentally reshaping the manufacturing world:
1. Skyrocketing Productivity
Automated systems and robots are tireless. They don't get fatigued, need breaks, or have off days. This continuous operation translates directly to significantly higher output rates compared to manual processes. A robotic welding cell, for example, can crank out hundreds of precise welds per hour, consistently, day in and day out—far outstripping human capabilities over extended shifts. This boost in productivity means bigger production volumes and a faster journey from concept to market.
2. Unmatched Precision and Quality
Robots, programmed to execute tasks with micro-millimeter accuracy, virtually eliminate human error in repetitive or intricate operations. The result? Dramatically improved product quality and consistency. In delicate electronics assembly, robots place tiny components with accuracy impossible for human hands, drastically cutting defects and rework. Higher quality means fewer warranty claims and a shining brand reputation.
3. Serious Cost Reduction and ROI
While the initial investment can seem hefty, the long-term cost savings from automation and robotics are incredibly compelling. These savings stem from:
- Reduced Labor Dependence: Fewer manual hours needed for monotonous or dangerous tasks.
- Less Waste: Precision work means less material waste and fewer flawed products.
- Optimized Energy Use: Modern automated systems are designed for lean energy consumption.
- Increased Output: You get far more production capacity without proportionate increases in overhead.
4. A Safer Workplace for Everyone
Robots can step into the breach for tasks that are dull, dirty, or outright dangerous for human workers. This includes extreme temperatures, handling hazardous materials, repetitive heavy lifting, or working in tight, risky spaces. By handing off these risks to robots, manufacturers dramatically improve worker safety, slash workplace injuries, and effortlessly meet stringent safety regulations. It also leads to a happier, healthier, and more satisfied workforce.
5. Enhanced Flexibility and Adaptability
The latest generation of robots boasts remarkable flexibility. Collaborative robots (cobots) can be easily reprogrammed and redeployed for different tasks, making them perfect for high-mix, low-volume production lines. Advanced automation systems can also be reconfigured with simple software updates, allowing manufacturers to swiftly adapt to new product designs, shifting market demands, or tweaked production schedules without costly retooling or downtime. This agility is non-negotiable in today's fast-moving global markets.
Real-World Applications Across Industries
The impact of automation and robotics is visible everywhere you look:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Robotic arms handle everything from welding and painting to assembly and quality inspection, underpinning mass production.
- Electronics Manufacturing: High-precision automation and robotics are indispensable for assembling intricate components, testing circuit boards, and packaging devices.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Robotic systems assist in surgeries, dispense medications, automate lab processes, and even manage hazardous biological samples, ensuring sterility and accuracy.
- Logistics and Warehousing: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), and robotic picking systems revolutionize inventory management, order fulfillment, and material transport.
- Food and Beverage: Automation guarantees consistent mixing, bottling, packaging, and quality control, while robots handle delicate produce or repetitive packing tasks.
- Aerospace: High-accuracy robotics is leveraged for assembling massive airframe components, drilling, riveting, and inspecting complex parts where precision is paramount.
Navigating the Challenges and Strategic Considerations
While the advantages are clear, bringing automation and robotics into your operations isn't without its hurdles. Manufacturers need to approach these considerations strategically:
1. The Initial Investment Can Be Significant
The upfront capital expenditure for purchasing, integrating, and setting up automated systems and robots can be substantial. This demands meticulous financial planning, a thorough ROI analysis, and often, phased implementation strategies to manage cash flow.
2. Workforce Transformation and Upskilling is Key
Introducing automation and robotics inevitably changes job roles. Repetitive manual tasks might diminish, which means you'll need to retrain and upskill your existing workforce. This requires investing in training programs to equip employees with new skills in robot operation, maintenance, programming, and data analysis.
3. Maintenance, Integration, and Cybersecurity are Constant Needs
Automated systems and robots aren't "set it and forget it." They demand regular maintenance to ensure peak performance and longevity. Plus, integrating new automated solutions with existing legacy systems can be complex. Finally, as systems become more interconnected, cybersecurity becomes paramount, demanding robust protocols to protect sensitive data and prevent operational disruptions.
4. You Must Be Adaptable and Continuously Improve
The technological landscape is always shifting. Manufacturers need to cultivate a culture of continuous improvement and be ready to adapt their automation strategies as new technologies emerge. This means regularly assessing performance, actively seeking optimization opportunities, and staying current with advancements in AI, machine learning, and advanced robotics.
The Future Trajectory: Smarter, More Autonomous Manufacturing
The future of automation and robotics is deeply intertwined with breakthroughs in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies are shattering previous limitations, leading us toward:
- Smarter, Truly Autonomous Systems: Future systems will learn from their environments, adapt to unforeseen situations, and make complex decisions in real-time.
- Seamless Human-Robot Collaboration: Cobots are just the beginning. The next generation will feature even more intuitive interfaces and advanced safety features, allowing for effortless and highly efficient collaboration between people and robots.
- Predictive Maintenance and Self-Optimization: AI-driven analytics will empower automated systems to forecast potential failures, scheduling maintenance proactively and even fine-tuning their own performance.
- Hyper-Personalization and Mass Customization: Advanced automation will make it easier for manufacturers to produce highly customized products at mass production scales.
- Digital Twins and Virtual Commissioning: Creating virtual replicas of physical systems allows you to simulate, test, and optimize manufacturing processes in a virtual environment before any physical implementation, dramatically cutting development time and costs.
This evolution will further blur the lines between traditional automation and robotics, ushering in a new era of highly intelligent, interconnected, and incredibly efficient manufacturing processes.
Conclusion: Empowering Manufacturing Through Precision and Strategy
To wrap things up, grasping the precise distinction between automation and robotics isn't just an academic exercise—it's a critical strategic move for businesses aiming to modernize their operations and carve out a powerful competitive advantage. While automation broadly covers any technology designed to minimize human input in tasks, robotics specifically zeroes in on programmable physical machines built to execute complex tasks and interact with their environment.
When you thoughtfully integrate both automation and robotics, you unleash a potent synergy, unlocking unprecedented levels of productivity, precision, cost savings, and safety in manufacturing. From automotive giants to nimble electronics producers, the benefits are undeniable. As the Fourth Industrial Revolution continues to unfold, powered by AI and advanced connectivity, the boundary between these two domains will become increasingly fluid, giving rise to smarter, more adaptable, and ultimately, more profitable manufacturing ecosystems.
At Kingstone Robotics, we stand at the forefront of this revolution. We specialize in delivering cutting-edge robotic solutions meticulously crafted to fit your unique manufacturing needs. Whether you're looking to fine-tune a single process or embark on a complete factory transformation, our expertise in leveraging the power of automation and robotics can help you redefine your operational capabilities.
Ready to unlock the full potential of your manufacturing operations and drive your business towards a more efficient, productive, and prosperous future? Contact Kingstone Robotics today.